Freshwater Aquarium Necklace Charm
$24.99
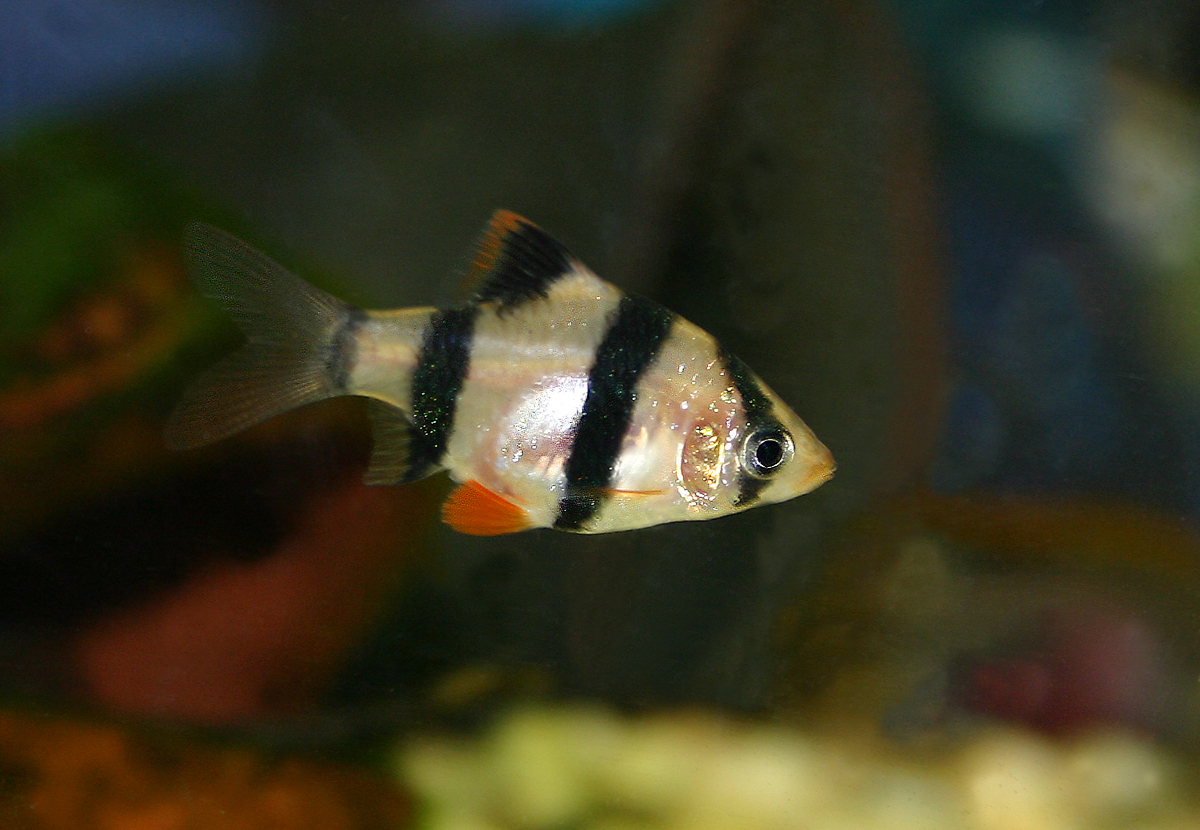

Puntigrus tetrazona
Reviewed for accuracy · Last updated Jan 2, 2026, 3:48 PM
Tiger Barbs are active, fast-swimming schooling fish known for fin-nipping behavior, especially when kept in small or unbalanced groups.
Freshwater
Moderate
Easy
32 gal (120 L)
3 in (6.5 cm)
5–7 years
Omnivore
Resident
Tiger Barbs are best kept in groups of at least six individuals. Larger groups help diffuse aggression and reduce fin-nipping behavior. Small groups often result in increased harassment of tank mates.
They are compatible with fast-moving, robust fish of similar size. Danios, loaches, and other barbs generally coexist without major issues. Tank mates should be able to tolerate constant activity.
Avoid slow or long-finned species such as bettas or angelfish. These fish are frequent targets for fin nipping. Proper stocking and tank size are key to peaceful coexistence.
Tiger Barbs thrive in well-oxygenated freshwater aquariums with stable water parameters and moderate water flow. They are highly active swimmers and require ample horizontal space to display natural schooling behavior. A longer tank is preferred over tall setups to support constant movement.
The aquarium should include fine gravel or sand substrate paired with hardy plants and driftwood. Plants help break lines of sight and reduce aggression within the group. Open swimming areas are essential to prevent stress and overcrowding.
Stable temperature and regular water changes are critical for long-term health. They tolerate a range of conditions but react poorly to sudden parameter shifts. Consistent maintenance greatly reduces stress-related aggression.
Tiger Barbs are omnivorous and accept a wide variety of foods in captivity. A high-quality flake or micro pellet should form the base of their daily diet. This ensures balanced nutrition and consistent growth.
Supplementation with live or frozen foods is highly beneficial. Bloodworms, brine shrimp, and daphnia enhance coloration and activity levels. These protein-rich foods should be offered several times per week.
Vegetable matter is also important for digestive health. Blanched spinach, zucchini, or spirulina-based foods are well accepted. Feeding small portions multiple times daily prevents overeating.
Breeding Tiger Barbs is achievable in home aquariums with proper preparation. A separate breeding tank with soft, slightly acidic water is recommended. Dense plants or spawning mops provide surfaces for egg scattering.
Conditioning adults with live foods improves spawning success. Spawning usually occurs in the early morning after a temperature increase. Females scatter hundreds of eggs which are fertilized externally.
Parents do not provide care and may eat the eggs if not removed. Eggs hatch within two days, and fry become free-swimming shortly after. Infusoria and fine fry foods support early growth.
Some links on this page may earn Fishmetry a commission at no extra cost to you.